Email enquiries@travel-doc.com
Email enquiries@travel-doc.com
Hepatitis A is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis A virus. It is spread through contaminated water and food, especially shellfish or through person to person contact where personal hygiene is poor (faecal-oral route).
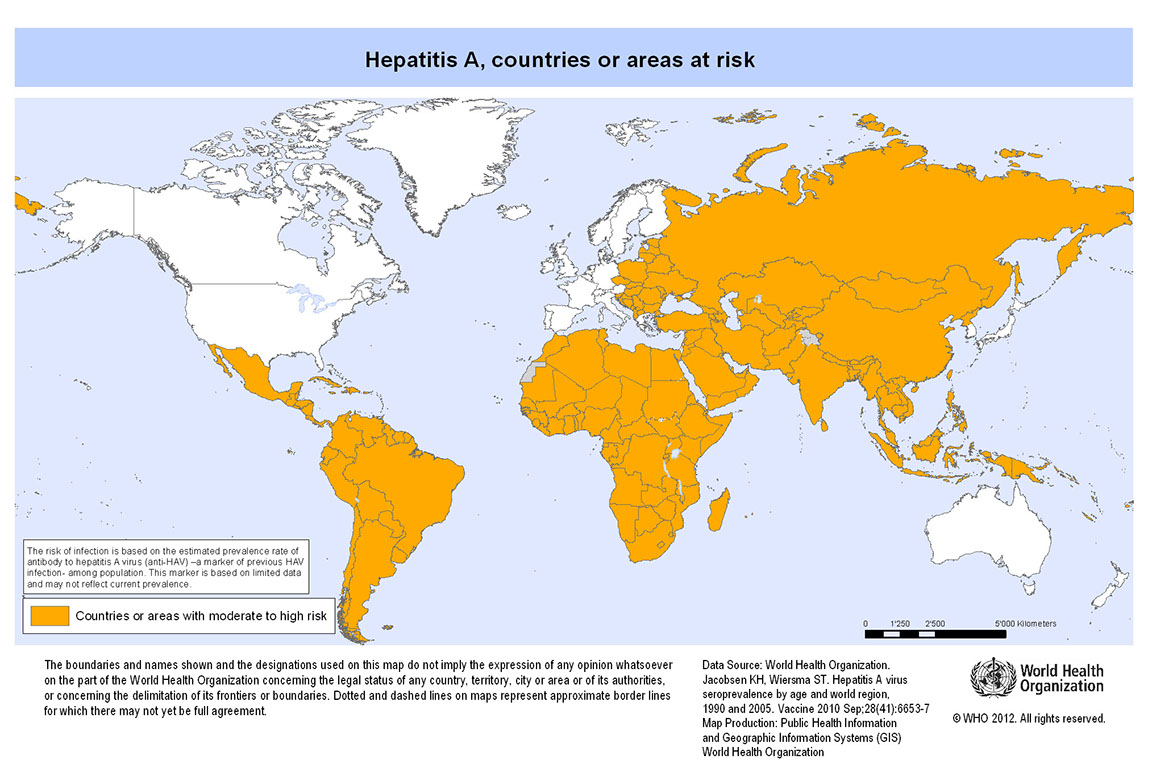
Hepatitis A occurs worldwide, mostly in countries where sanitation is poor. It is now rare in Western Europe, Scandinavia, North America, Japan, New Zealand and Australia. Most cases imported into Britain have been contracted in the Indian sub-continent.
Vaccination is recommended if you are visiting areas where drinking water may be unsafe and where hygiene and sanitation is poor. There are various brands of hepatitis A vaccine available: Avaxim, Epaxal, Havrix Monodose, Havrix Junior Monodose and Vaqta Paediatric.
Hepatitis A vaccine is also available in a preparation that combines it with hepatitis B vaccine: Ambirix, Twinrix and Twinrix Paediatric and a preparation that combines it with typhoid vaccine: Hepatyrix and ViATIM.
Prevention is focused on ensuring that food and water are safe. Avoidance of foodstuffs such as shellfish, salads, unwashed fruit and vegetables and raw or undercooked meat products are essential.
Good personal hygiene is also very important. Individuals should ensure that they wash their hands prior to eating and after using the bathroom.
Children often asymptomatic. Symptoms are common in adults and severity tends to increase with age.
Onset of illness is usually abrupt with:
©WHO
Back to Top