Email enquiries@travel-doc.com
Email enquiries@travel-doc.com
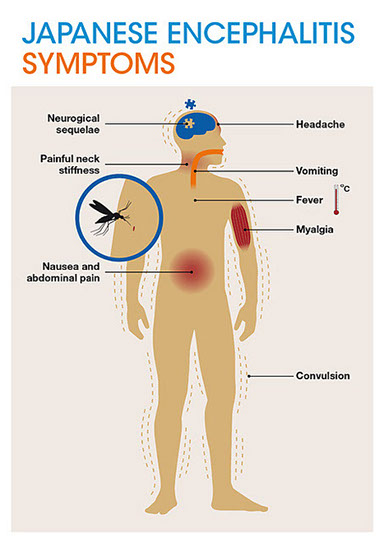
Japanese encephalitis symptoms
Japanese encephalitis can be a serious illness causing inflammation of the brain. You should consider being immunised against Japanese encephalitis before you travel to certain countries in Southeast Asia and the Far East.
Check with your practice nurse at least 6-8 weeks before you travel to see if you should have this immunisation.
Japanese encephalitis is caused by a virus. It is passed to humans by the bite of infected mosquitoes. It cannot be transmitted by other humans.
Japanese encephalitis is usually a mild illness. In many cases there are no symptoms. However, in a small number of cases (about 1 in 200 infected people) the illness is much more serious. In these people, the infection may start with fever, tiredness, headache, vomiting, and sometimes confusion and agitation. This may progress to encephalitis (inflammation of the brain). This can cause permanent brain damage and is fatal in some cases.
Japanese encephalitis occurs throughout Southeast Asia and the Far East. It is mainly a problem in rural farming areas. It occurs more commonly in the rainy season (roughly May-September) when the mosquitoes are most active.
Your doctor or practice nurse can advise if you should have this immunisation for your travel destination.
Generally, it is advised for travelers who stay for a month or longer during the transmission season in rural areas of certain countries in Southeast Asia and the Far East. It may be advised for shorter trips to these countries if you are at particular high risk. For example, if you travel to areas where rice and pig farming co-exist or if you do a lot of outdoor activities.
The vaccine stimulates your body to make antibodies against the virus. These antibodies protect you from illness should you become infected with this virus.
In May 2009, a new Japanese encephalitis vaccine, Ixiaro®, became available. This is the vaccine recommended in the UK. It is licensed for use in infants aged 2 months, and older. This is usually given as two injections; the second injection is given 28 days after the first. Full immunity takes up to a month to develop. The course of injections should be completed at least one week before departure. So, you should see your practice nurse well in advance of your travel date.
A booster dose should then be given within the second year after the initial course of two injections.

The IXIARO vaccine
IXIARO vaccine costs only £125 per dose at TravelDoc™.
The primary schedule consists of two vaccines 28 days apart.
An accelerated schedule for adultscan be given 7 days apart.
The vaccine is not live and is therefore easily tolerated.
There is no cure for Japanese Encephalitis.
It should be considered for travellers to South East Asia, for example India, Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, China, Indonesia, Bali, Malaysia, Phillipines.
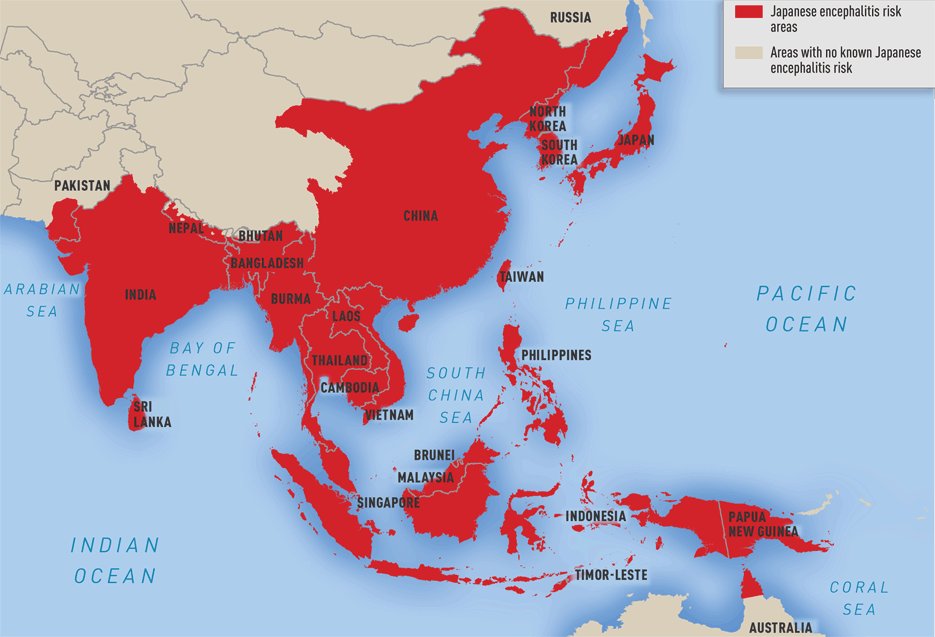
Geographic distribution of Japanese encephalitis virus ®CDC